
Molecular Structure
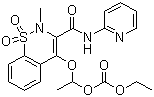
Piroxicam Betacyclodextrine
Molecular Formula C20H21N3O7S
Molecular Weight 447.46
CAS Registry Number 96684-40-1
Piroxicam-beta-cyclodextrin is a complex of the established nonsteroidal
antiinflammatory drug (NSAID) piroxicam and an inert cyclic
macromolecule, beta-cyclodextrin. In clinical trials in patients with
rheumatic diseases or pain arising from other conditions, it was as
effective an analgesic as standard piroxicam, and showed a faster onset
of action on the first day of treatment. In short term pharmacodynamic
studies in healthy volunteers, piroxicam-beta-cyclodextrin was
equivalent to or tended to show less gastrointestinal mucosal toxicity
than standard piroxicam, as assessed by endoscopy and faecal blood loss.
However, no data are available on its comparative gastrointestinal
mucosal effects from long term clinical trials using similar measures.
Preliminary findings from a clinical study suggest
piroxicam-beta-cyclodextrin caused fewer gastroduodenal lesions than
tenoxicam. As with other NSAIDs, the majority of adverse events
associated with piroxicam-beta-cyclodextrin in clinical trials were
gastrointestinal in origin, with epigastric pain, heartburn and nausea
the most common. Thus, piroxicam-beta-cyclodextrin is an effective agent
in patients with rheumatic diseases or other pain states. When rapid
analgesia is required in the initial treatment of acute pain, the faster
onset of action of piroxicam-beta-cyclodextrin may be an advantage over
the parent compound; however, this is unlikely to be important during
long term therapy. The results of further long term trials are awaited
before firm conclusions can be reached regarding the gastrointestinal
tolerability of piroxicam-beta-cyclodextrin compared with that of
standard piroxicam and other NSAIDs.
|
|








